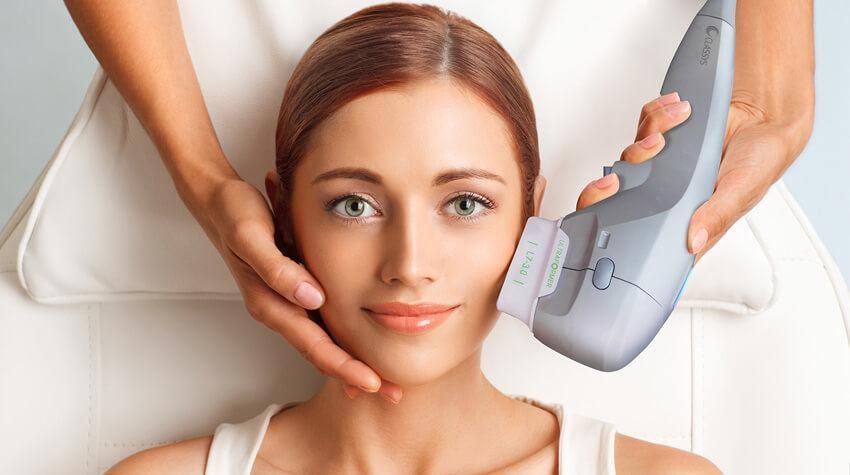
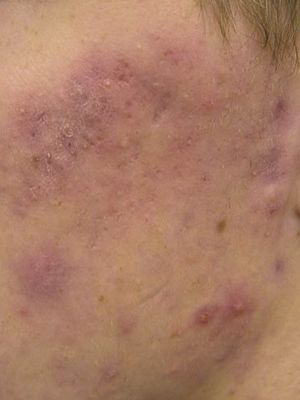
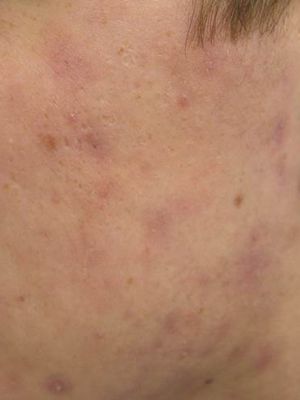
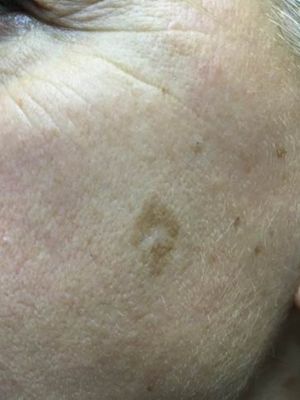
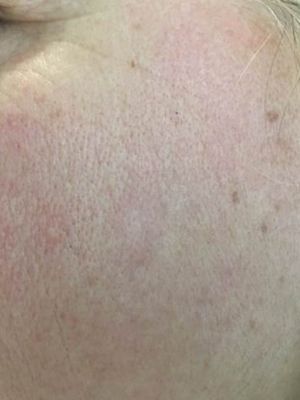
Our Services
Discover a comprehensive range of beauty and wellness services tailored to enhance your natural glow. From rejuvenating skin treatments to advanced body sculpting, our expert team is here to help you achieve your beauty goals with personalized care and the latest technologies.
Our Blog
Delve into our blog, where we share the latest industry insights, expert tips, and guides on innovative treatments. Discover a wealth of knowledge curated to keep you informed and inspired about the beauty and wellness trends driving the med spa and laser clinic landscape.
What Our Clients Have To Say
Discover authentic feedback from our happy clients who have experienced our top-notch services. Their stories highlight our dedication to quality and customer satisfaction. Join them in achieving glowing results. Read on to see why Glow & Go Med Spa & Laser Clinic is trusted by many.