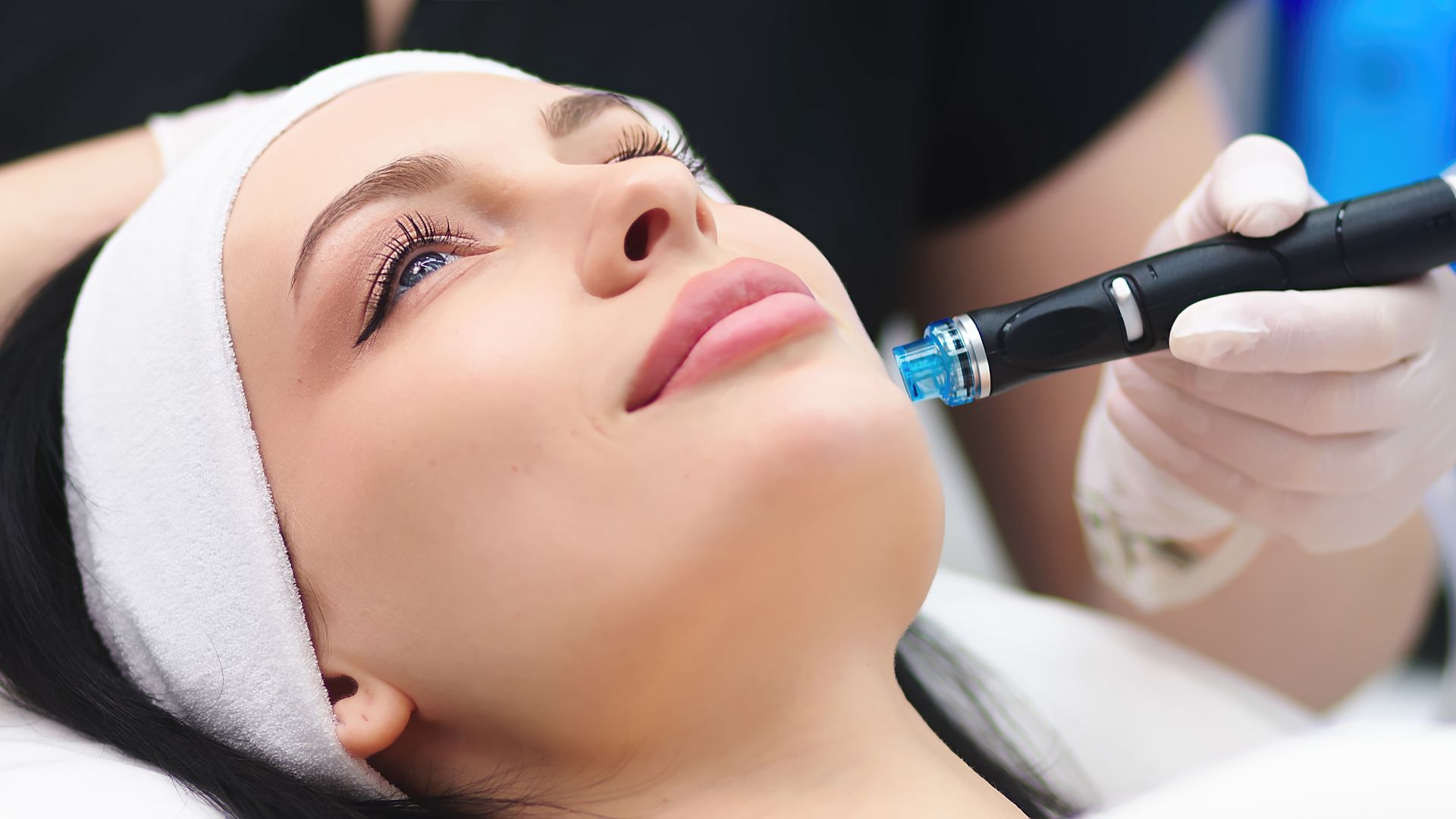
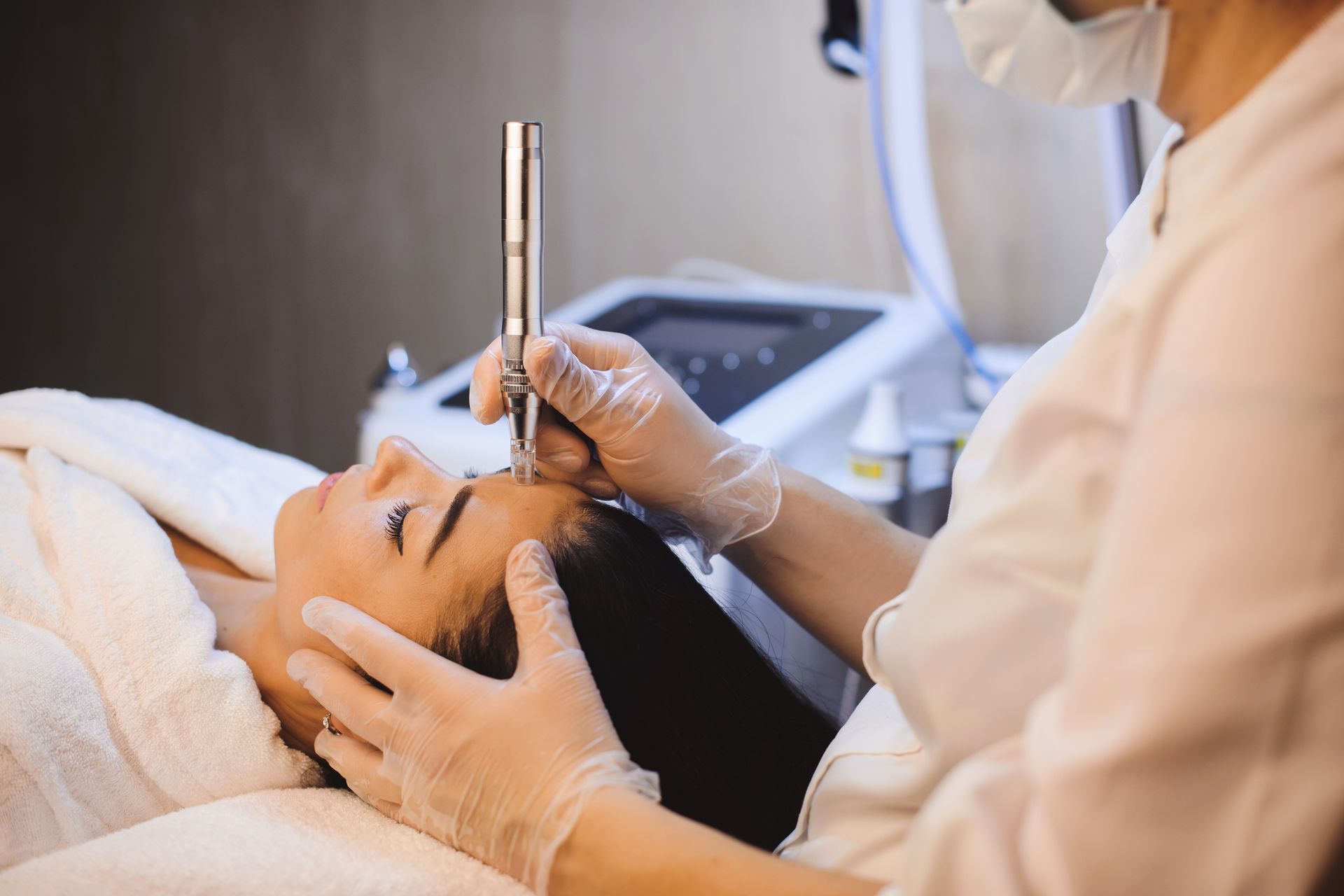
Get In Touch
Call: (343) 630-0004
Email: bushra@glowgo.ca
Address: 592 Rathburn Road West, Mississauga, Ontario L5B 3A4, Canada
Business Hours
- Mon, Wed, Thu, Fri
- -
- Tuesday
- Closed
- Saturday
- -
- Sunday
- Closed
*Sunday by Appointment Only
Glow & Go Med Spa & Laser Clinic
Address
592 Rathburn Road West, Mississauga, Ontario L5B 3A4, Canada
Phone
Business Hours
- Mon, Wed, Thu, Fri
- -
- Tuesday
- Closed
- Saturday
- -
- Sunday
- Closed
*Sunday - By Appointment Only
© 2026
Glow & Go Med Spa & Laser Clinic